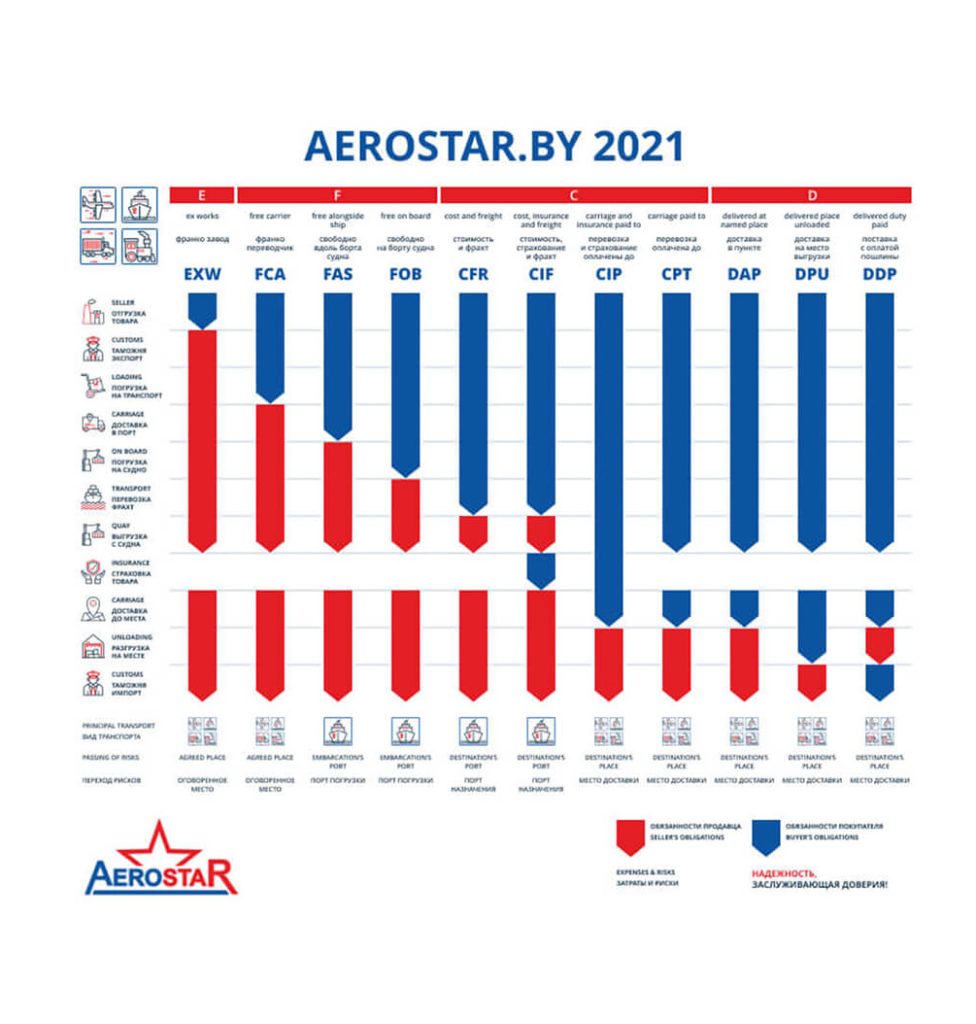
| Duties of a salesperson | Buyer’s responsibilities | |
| EXW Ex Works — Franco plant |
Prepares goods and ships them | Performs customs clearance for export and import, delivers cargo |
| FCA Free Carrier — «Франко перевозчик» |
Carries out customs clearance for export. Ships the goods to the trucking company chosen by the buyer |
Delivers cargo and conducts customs clearance for imports |
| FAS Free Alongside Ship — “Free along the side of the ship.” |
Handles export clearance. Places the cargo at the port of shipment near the vessel of the buyer’s choice | Loads the goods on board the vessel. Delivers the goods to the port of discharge. Carries out import clearance |
| FOB Free On Board — “Free on board.” |
Carries out export clearance. Delivers the cargo to the port of shipment and loads it on the board that the buyer specifies | Delivers the cargo to the port where unloading will take place. Arranges import clearance |
| CFR Cost and Freight — “Cost and Freight.” |
Exports goods and loads them on board and delivers them to the port of discharge | Unloads and receives cargo at the port of discharge. Performs import clearance |
| CIF Cost, Insurance and Freight — “Cost, Insurance and Freight.” |
Formalizes the cargo for export, insures it in favor of the seller. The insurance should minimally cover the risks. Delivers the goods to their destination | Unloads and receives cargo, clears for importation |
| CIP Carriage and Insurance Paid to — “Freight/transportation and insurance paid up to” |
Formalizes the cargo for export, insures it in favor of the seller. The insurance should cover all possible risks to the maximum extent possible. Delivers the goods to their destination | Unloads cargo, clears for import. |
| CPT Carriage Paid To – “Freight/transportation paid to” |
Exports the goods for export, delivers them to their destination | Unloads cargo, clears for import. |
| DAP Delivered At Point — “Delivered at point.” |
Organizes cargo for export, delivers it to the specified destination | Unloads cargo, clears for import. |
| DPU Delivered Named Place Unloaded — “Delivered to the unloading site.” |
Conducts customs clearance for export, delivers cargo to destination and unloads it | Принимает груз и оформляет на импорт |
| DDP Delivered Duty Paid — “Delivered with payment of duty” |
Carries out export clearance. Delivers the cargo to the specified place, after which it is cleared for import and duty is paid | Receives cargo and clears for importation |
Incoterms
Incoterms are eleven international rules that are used in national and international trade. They are recognized by customs authorities, legal organizations and entrepreneurs in all countries of the world.
Incoterms rules are a special designation of trade terms in the form of abbreviations by the first three letters. Each abbreviation has its own decoding and reflects business practice in the international delivery of goods from seller to buyer.
Incoterms define the rights and obligations between the parties involved in the contract of sale in terms of the terms of delivery of cargo.
Incoterms are the basic terms and conditions for international trade in goods.
Group E – shipment.
Group F – principal transportation is paid by the buyer.
Group C – main carriage paid by the seller.
Group D – delivery.
Change in Incoterms 2020
Incoterms are the rules adopted in the sphere of national and international trade. They are a standard and represent terms in the form of 11 abbreviations, which have their own decoding. The terms are also classified by mode of transportation.
The updated version still refers to the rights and obligations of persons involved in foreign economic relations. But it gives a detailed description of what to rely on when choosing a term for a particular transaction. The new version also outlines how a trade contract relates to additional obligations.
FCA term supplements
In the 2020 edition, FCA may be used instead of FOB for containerized maritime transportation. In this case, the seller has the right to transfer the container with the export goods to the buyer before the carrier loads the goods onto the ship.
The use of FCA relieves the seller from additional obligations to the buyer in terms of concluding an agreement for the transportation of the cargo.
Please note. Incoterms 2020 gives each of the parties involved the opportunity to negotiate the transaction. The buyer instructs the carrier to sign and issue a bill of lading for the seller after loading the goods on board. The seller transfers the issued bill of lading to the buyer through a banking institution.
Introduction of export cargo insurance clauses in CIF and CIP terms
The terms CIF and CIP oblige the seller to insure the export cargo.
In the 2020 regulations, CIF requires the seller to carry minimum insurance. Higher rates are negotiated optionally based on the contract.
If CIP is used, the seller provides the maximum level of cargo insurance against all possible risks: sinking and capsizing of the vessel, collision, grounding, fire, explosion, unloading at a port of distress. In this case only low rates are optionally agreed.
Maintaining the DPU term
From 2020, DPU is used instead of DAT – delivery to the discharge point, not to the terminal as was the case in version 2010.
What is the difference between unloading place and terminal:
The seller gets the option to unload not at a specific terminal, but at any location designated for delivery of goods. But a specific terminal can also be selected.
The term DPU also implies that the unloading of the cargo remains the responsibility of the seller. The buyer only accepts the goods and carries out the necessary customs clearance for import.
Use of seller’s and buyer’s transportation for trucking purposes
In the 2010 edition, the transportation of goods is handled by a third party, the carrier. Both parties can hire a contractor.
In most cases, transportation is organized without the participation of third-party logistics companies. Goods are transported on the transport of either party to the contract. So both parties to the contract can use their own vehicle for transportation. This is directly stated in the terms of group D. This does not exclude the possibility of contracting for transportation by a third party.
Clarification of delivery terms
In the updated rules, the terms of delivery and other obligations of the parties have been clarified as much as possible:
Each term consists of two sections of ten articles each. The document details the obligations of the parties to the trade agreement, general obligations related to transportation, insurance, delivery, customs documentation, cost allocation, etc. The structured rules help to see at a glance all costs incurred by the seller and the buyer.
Structured rules help to see at a glance all expenses of both the seller and the buyer.
In the new version, a special section “Cost Allocation” has been created, which takes into account the nuances of costs. This allows the parties to the contract not to look for separate costs in different items.
The structure of the 2020 rules also makes it as convenient as possible to compare the responsibilities of each party for all delivery points.
Notice. Regardless of the terms of delivery, the seller must follow the safety rules for the operation of transport and transportation of goods. The seller must explain to the buyer that certain requirements are mandatory for the organization of cargo transportation.
Important.
Incoterms 2020 states that if the risk of transportation is transferred in the seller’s country, the buyer is responsible for customs transit formalities. The rule applies in the opposite direction as well.
Use of Incoterms in foreign trade contracts:
When a transaction is concluded between two parties, the 2020 rules must be specified in the contract. The reference is specifically to the new edition.
It is not necessary to put in the document